What is a Staph Infection?
Staphylococcus aureus, commonly found on the skin and in the nose, usually coexists harmlessly with our bodies. However, when it infiltrates through cuts or wounds, it can lead to various infections, ranging from superficial skin conditions to life-threatening complications like pneumonia and sepsis.
Signs and Symptoms of Staph Infections:
Recognizing the signs and symptoms is crucial for prompt intervention. Boils, characterized by painful, pus-filled lumps, impetigo, manifesting as oozing sores, and cellulitis, resulting in warm, swollen red patches, are prevalent skin infections caused by staph bacteria. In severe cases, symptoms like fever, low blood pressure, and a rapid heartbeat may manifest, necessitating immediate medical attention to avert further complications.
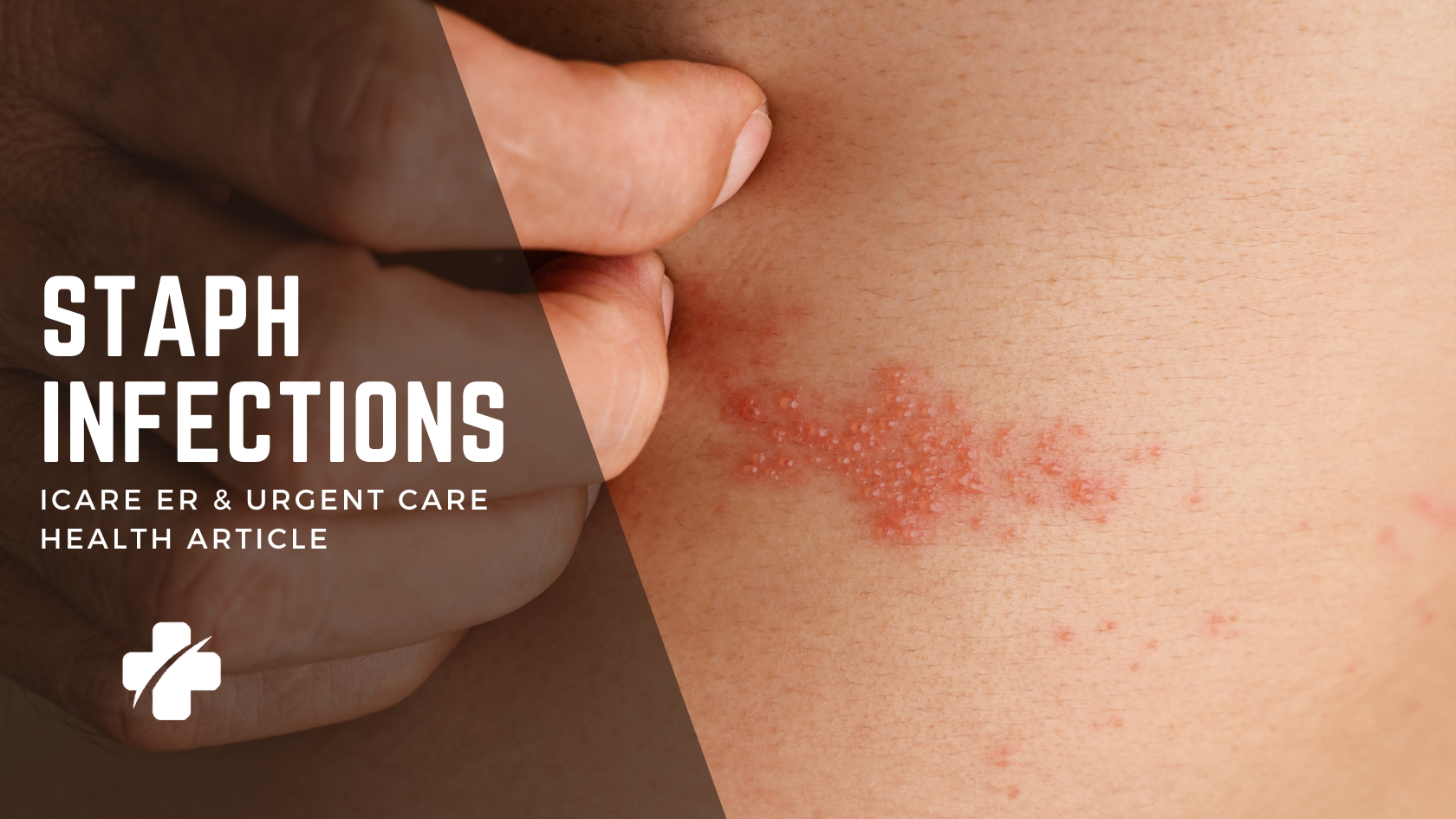
What Does a Staph Infection Look Like?
The appearance of a staph infection is diverse, depending on its type and severity. Boils, filled with painful pus, impetigo, manifesting as oozing sores, and cellulitis, resulting in warm, swollen red patches, are common skin infections caused by staph bacteria. Severe cases can induce symptoms like fever, low blood pressure, and a rapid heartbeat, necessitating immediate medical attention to prevent further complications.
How Do Staph Infections Spread?
Understanding how staph infections spread is crucial in preventing their escalation. Staph bacteria are highly contagious and can be transmitted through direct skin-to-skin contact, contaminated surfaces, or shared personal items like towels and razors. Additionally, crowded and unsanitary environments can facilitate the rapid spread of staph infections, making it essential to practice good hygiene and maintain clean surroundings.
How to Combat Staph Infection Spread Without Antibiotics?
While antibiotics remain the primary treatment for staph infections, complementing them with preventive measures is essential. Here are some strategies:
- Topical Antiseptics: Applying antiseptics like tea tree oil or honey may hinder the spread of staph bacteria on the skin. However, it’s crucial to consult a healthcare professional before relying solely on these methods, especially in severe cases.
- Wound Care: Proper wound care is a key player in preventing staph infections. Keep wounds clean, dry, and covered to minimize the risk of bacterial entry. Regularly changing dressings and maintaining good hygiene are paramount in wound management.
- Probiotics: Some studies suggest that probiotics may contribute to balancing the body’s microbial environment, potentially reducing the risk of staph infections. Incorporating probiotic-rich foods or supplements may be considered, but always consult with a healthcare provider for personalized advice.
Conclusion: Staph infections are not to be taken lightly, and swift action is crucial. If you suspect a staph infection, contact your healthcare provider or visitor of our iCare ER & Urgent Care locations for an assessment and appropriate treatment. Understanding how staph infections spread empowers you to take proactive measures, reinforcing the importance of good hygiene and a clean environment in preserving your health.